How to convert watts to VA
How to convert real power in watts (W) to apparent power in volt-amps (VA).
Watts to VA calculation formula
The apparent power S in volt-amps (VA) is equal to the real power P in watts (W), divided by the power factor PF:
S(VA) = P(W) / PF
So volt-amps are equal to watts divided by the power factor.
volt-amps = watts / PF
or
VA = W / PF
How to convert VA to watts
How to convert apparent power in volt-amps (VA) to real power in watts (W).
VA to watts calculation formula
The real power P in watts (W) is equal to the apparent power S in volt-amps (VA), times the power factor PF:
P(W) = S(VA) × PF
So watts are equal to volt-amps times the power factor.
watts = volt-amps × PF
or
W = VA × PF
Example
What is the real power in watts when the apparent power is 3000 VA and the power factor is 0.8?
Solution:
P = 3000VA × 0.8 = 2400W
Power Factor
In AC circuits, the power factor is the ratio of the real power that is used to do work and the apparent power that is supplied to the circuit.
The power factor can get values in the range from 0 to 1.
When all the power is reactive power with no real power (usually inductive load) - the power factor is 0.
When all the power is real power with no reactive power (resistive load) - the power factor is 1.
Power factor definition
The power factor is equal to the real or true power P in watts (W) divided by the apparent power |S| in volt-ampere (VA):
PF = P(W) / |S(VA)|
PF - power factor.
P - real power in watts (W).
|S| - apparent power - the magnitude of the complex power in volt⋅amps (VA).
Power factor calculations
For sinusuidal current, the power factor PF is equal to the absolute value of the cosine of the apparent power phase angle φ (which is also is impedance phase angle):
PF = |cos φ|
PF is the power factor.
φ is the apprent power phase angle.
The real power P in watts (W) is equal to the apparent power |S| in volt-ampere (VA) times the power factor PF:
P(W) = |S(VA)| × PF = |S(VA)| × |cos φ|
When the circuit has a resistive impedance load, the real power P is equal to the apparent power |S| and the power factor PF is equal to 1:
PF(resistive load) = P / |S| = 1
The reactive power Q in volt-amps reactive (VAR) is equal to the apparent power |S| in volt-ampere (VA) times the sine of the phase angle φ:
Q(VAR) = |S(VA)| × |sin φ|
Single phase circuit calculation from real power meter reading P in kilowatts (kW), voltage V in volts (V) and current I in amps (A):
PF = |cos φ| = 1000 × P(kW) / (V(V) × I(A))
Three phase circuit calculation from real power meter reading P in kilowatts (kW), line to line voltage VL-L in volts (V) and current I in amps (A):
PF = |cos φ| = 1000 × P(kW) / (√3 × VL-L(V) × I(A))
Three phase circuit calculation from real power meter reading P in kilowatts (kW), line to line neutral VL-N in volts (V) and current I in amps (A):
PF = |cos φ| = 1000 × P(kW) / (3 × VL-N(V) × I(A))
Power factor correction
Power factor correction is an adjustment of the electrical circuit in order to change the power factor near 1.
Power factor near 1 will reduce the reactive power in the circuit and most of the power in the circuit will be real power. This will also reduce power lines losses.
The power factor correction is usually done by adding capacitors to the load circuit, when the circuit has inductive components, like an electric motor.
Power factor correction calculation
The apparent power |S| in volt-amps (VA) is equal to the voltage V in volts (V) times the current I in amps (A):
|S(VA)| = V(V) × I(A)
The reactive power Q in volt-amps reactive (VAR) is equal to the square root of the square of the apparent power |S| in volt-ampere (VA) minus the square of the real power P in watts (W) (pythagorean theorem):
Q(VAR) = √(|S(VA)|2 - P(W)2)
Qc (kVAR) = Q(kVAR) - Qcorrected (kVAR)
The reactive power Q in volt-amps reactive (VAR) is equal to the square of voltage V in volts (V) divided by the reactance Xc:
Qc (VAR) = V(V)2 / Xc = V(V)2 / (1 / (2πf(Hz)×C(F))) = 2πf(Hz)×C(F)×V(V)2
So the power factor correction capacitor in Farad (F) that should be added to the circuit in parallel is equal to the reactive power Q in volt-amps reactive (VAR) divided by 2π times the frequency f in Hertz (Hz) times the squared voltage V in volts (V):
C(F) = Qc (VAR) / (2πf(Hz)·V(V)2)
Electric Power
Electric power is the rate of energy consumption in an electrical circuit.
The electric power is measured in units of watts.
- Electric power definition
- Electric power calculation
- Power of AC circuits
- Power factor
- Power calculator
Electric power definition
The electric power P is equal to the energy consumption E divided by the consumption time t:
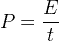
P is the electric power in watt (W).
E is the energy consumption in joule (J).
t is the time in seconds (s).
Example
Find the electric power of an electrical circuit that consumes 120 joules for 20 seconds.
Solution:
E = 120J
t = 20s
P = E / t = 120J / 20s = 6W
Electric power calculation
P = V ⋅ I
or
P = I 2 ⋅ R
or
P = V 2 / R
P is the electric power in watt (W).
V is the voltage in volts (V).
I is the current in amps (A).
R is the resistance in ohms (Ω).
Power of AC circuits
The formulas are for single phase AC power.
For 3 phase AC power:
When line to line voltage (VL-L) is used in the formula, multiply the single phase power by square root of 3 (√3=1.73).
When line to zero voltage (VL-0) is used in the formula, multiply the single phase power by 3.
Real power
Real or true power is the power that is used to do the work on the load.
P = Vrms Irms cos φ
P is the real power in watts [W]
Vrms is the rms voltage = Vpeak/√2 in Volts [V]
Irms is the rms current = Ipeak/√2 in Amperes [A]
φ is the impedance phase angle = phase difference between voltage and current.
Reactive power
Reactive power is the power that is wasted and not used to do work on the load.
Q = Vrms Irms sin φ
Q is the reactive power in volt-ampere-reactive [VAR]
Vrms is the rms voltage = Vpeak/√2 in Volts [V]
Irms is the rms current = Ipeak/√2 in Amperes [A]
φ is the impedance phase angle = phase difference between voltage and current.
Apparent power
The apparent power is the power that is supplied to the circuit.
S = Vrms Irms
S is the apparent power in Volt-amper [VA]
Vrms is the rms voltage = Vpeak/√2 in Volts [V]
Irms is the rms current = Ipeak/√2 in Amperes [A]
Real / reactive / apparent powers relation
The real power P and reactive power Q give together the apparent power S:
P2 + Q2 = S2
P is the real power in watts [W]
Q is the reactive power in volt-ampere-reactive [VAR]
S is the apparent power in Volt-amper [VA]
[참고 사이트]
https://www.rapidtables.com/convert/electric/va-to-watt.html
How to convert volt-amps (VA) to watts (W)
www.rapidtables.com
'기타' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 텍스트, 문서 파일 비교 (1) | 2022.09.19 |
|---|---|
| 파일 번역 사이트(무료) (0) | 2021.11.09 |
| Flash 메모리 (네이버 검색) (0) | 2021.09.29 |
| 생산과 시간 관련된 용어 정리 (0) | 2021.05.10 |
| 터치키는 어떻게 만들까? (0) | 2020.11.04 |


댓글